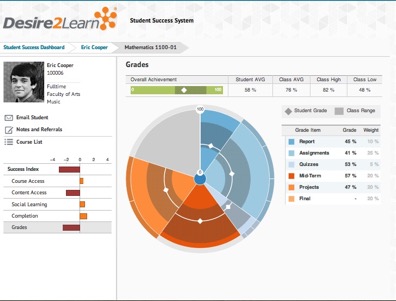
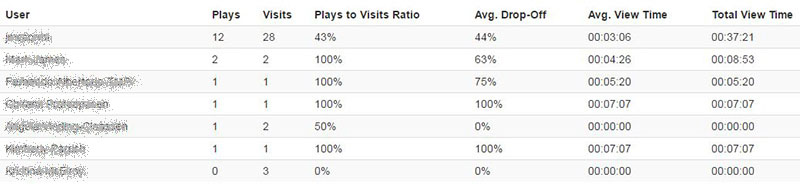
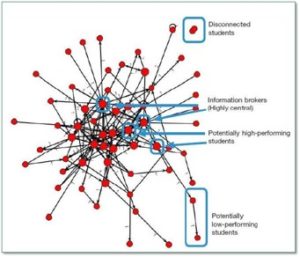
Lisa Spitz is an assistant professor at Lesley’s College of Art and Design and the program director for the User Experience online BS degree program. Lisa worked with eLIS this fall to pilot a peer feedback tool, called Peergrade, in her Sketching for Interactive Design course. Below she shares her and her students’ experiences using Peergrade.
In this course, students use sketching to document research insights, tell a story, and visualize mobile interface concepts and interactions. Each individual assignment includes a period of sketching and revising, where students provide peer feedback and then revise their own sketches for overall clarity. My initial experience teaching this course in Blackboard raised a number of challenges with the peer review process: not all peer feedback was of the same caliber and not all students received the same amount of feedback. This meant I was compensating for poor and/or incomplete feedback. I was also manually tracking the quality and quantity of feedback each student provided to their peers, for grading purposes. Further, due to inconsistencies in the types of feedback received, students reported finding it difficult to revise their work.
Over the summer, John McCormick in eLIS introduced me to an online peer review platform called Peergrade. The overall format and structure of Peergrade was a good match for my particular assignment structure and I was interested in seeing how it might better support our students in the peer review process.
The tool itself was fairly easy to learn. As an instructor, I was able to set up my “classroom” in Peergrade and create each of my assignments. For students, their experience entailed posting their sketches in Peergrade and then evaluating their peers’ sketches based on a custom rubric (which I set up in advance of the course running). The biggest challenge I faced was in tailoring the rubrics to each individual assignment. Students evaluated their peers work based on quantity and diversity of sketches as well as unique requirements for each assignment. The rubrics I created provided students with both quantitative and qualitative feedback on their sketches; and the system guaranteed that each student received feedback from three other students.
Students responded favorably to the use of Peergrade. They were fairly self-sufficient in using the Peergrade platform. It required very little technical support from my end; for instance, allowing late assignment submissions and permitting students to re-upload their work. Some adhoc quotes found in journal entries and the course evaluation include:
- “I really like Peergrade, I only wish the rest of my courses used this site. It is so much easier to give the feedback and receive the feedback that you want without upsetting another peer about your opinion. Since it is anonymous it is easier to be truthful if you have suggestions on changes.”
- “That program allowed me to finally get honest feedback from my peers on how they truly felt about my work.”
- “By reviewing other students, I often could improve my own work through just that process alone.”
- “The peer commenting system was a great way to discuss among other students each other’s work before turning in the final assignment each week. Critiquing helped me understand my own skills better.”
- “Peergrade was life changing, love it.”
In an ideal world, I’d spend more time user-testing assignment rubrics before launching these assignments with a live class. However, design is an iterative process and course design is no different and I anticipate refining each assignment rubric with each course instantiation.
If you’re just not sure how this would work within your classroom context, I’d say start small. Choose one project in which you’d like students to give and receive quality peer feedback. Decide what a “good” assignment submission looks like and set up your rubric to probe specifically on those areas. Then, see what the experience looks like from both the Instructor and Student views. Having an initial experience with Peergrade will help you to determine just how and when it might be an asset in your courses.
Peergrade is currently be used in a small number of online and on campus courses at Lesley. If you would like more information on using Peergrade or peer feedback in your courses, contact elis@lesley.edu.